Visit the Microscopy Shop!
>>> USA Shop | Germany Shop | UK Shop | Canada Shop <<<
As an Amazon Affiliate, I earn a commission but it does not cost you more.
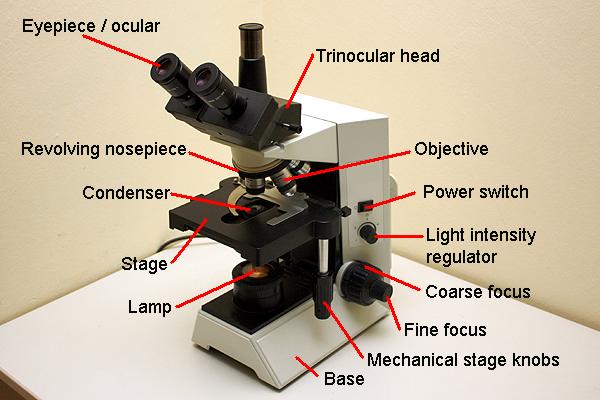
- The base: The base of the microscope supports all of the other parts. It is important for the stability of the microscope and contains the lamp.
- The stage: The specimen slide is placed on the stage. The stage has an opening to allow light to pass through. The slide can either be held by stage clips or by a slide holder which allows the moving of the slide by turning two knobs.
- The revolving nose piece: The nose piece holds the objectives. By turning the nose piece it is possible to rotate different objectives into position to view the specimen at different magnifications.
- The objectives: The objectives are one of the more expensive parts of a microscope. The contain several lenses and magnify the image.
- The eyepiece (ocular): You look through the eyepiece to see the magnified image. Most eyepieces magnify about 10x. Eyepieces are often placed loosely into the microscope’s tube, and can therefore be taken out easily. Some educational microscopes have the eyepiece fixed to prevent students from taking them out.
- The light source: There are several possibilities here. Halogen light and LEDs are most common these days. LEDs produce a cooler light of consistent color temperature. Halogen light has a richer color spectrum and therefore might provide advantages for seeing certain stains.
- The coarse focus knob: This knob raises and lowers the stage quickly. It should only be used with the low power objective (4x).
- The fine focus knob: Turn this knob to adjust the focus of the image when using the higher magnification objectives. Te fine focus knob is also used to bring the different parts of the specimen into focus. Te fine focus knob therefore allows you to “section through” the different depths of the specimen.
- The condenser: This is a lens system which is mounted right beneath the stage. The condenser focuses the light of the lamp onto the specimen. The condenser also has a diaphragm and a filter holder.
- The condenser diaphragm: This diaphragm controls the resolution and contrast of the image. As a side effect, it also changes the brightness of the image.
- The light intensity control: Te brightness of the lamp is controlled by turning or sliding the control. It is necessary to increase the light intensity when working with the higher power objectives.