Light emitting diodes are a nearly ideal microscopic light source for several reasons. A school should seriously consider purchasing these.
- Long life span: LEDs have a life span of approximately 50 000-100 000 hours. A microscope which is in operation an unrealistic 12 hours per day would have a life span of 20 years+. Unlike tungsten or halogen light bulbs, LED lamps do not need to be replaced and are practically maintenance free.
- Low energy use: The electrical power is converted 80% into light, with nearly no heat production. The efficiency is therefore very high. This makes it possible to operate microscopes with batteries and without a power supply. LED microscopes can therefore also be used in classrooms in which the tables do not have an electrical power outlet. Incandescent light bulbs, in contrast, only convert 20% of the electrical energy to light, the rest is lost as heat.
- Not sensitive to movement: Hot tungsten or halogen light sources should not be moved during operation and when they are hot. Movement reduces the lifespan of the bulb becasue a hot filament breaks more easily when exposed to shock. LEDs are insensitive to movement. Bumping the microscope when the LEDs are on will have no detrimental effect on the LED.
- Can be switched on at full power: Incandescent light bulbs should not be switched on with the light intensity setting at maximum level. Rather, one should slowly increase the intensity after turning the light on. Sending maximum current through a cold bulb will reduce its lifespan. LEDs are insensitive in this respect. Sending a current through
- No color drift with age: LEDs do not significantly change their color or intensity with increasing age. Traditional incandescent light bulbs will shift towards the red end of the spectrum as they age. This is because over time a thin matallic layer will deposit on the inside of the glass bulb. A slight color shift can also be observed with LEDs, this is due to the aging of the resin of the LED.
- Nearly no heat produced: LEDs produce a cool light. LEDs pose no danger of overheating the specimen. This is important when observing water samples with live organisms. A heated specimen will drive out oxygen from the water sample which may possibly reduce movement of some (heterotrophic) organisms.




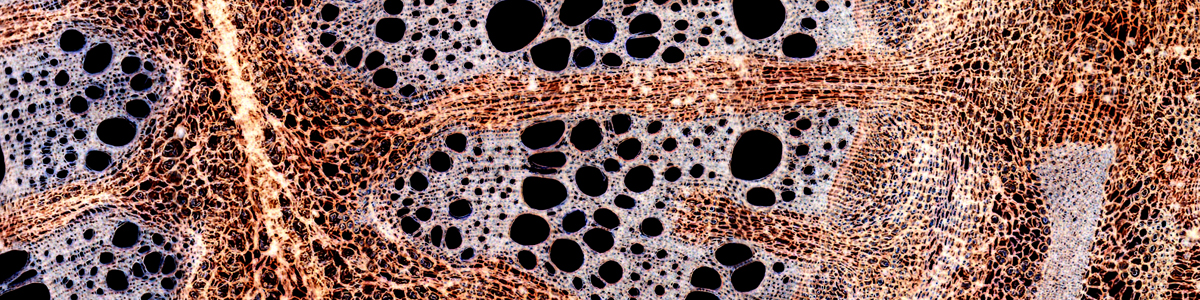
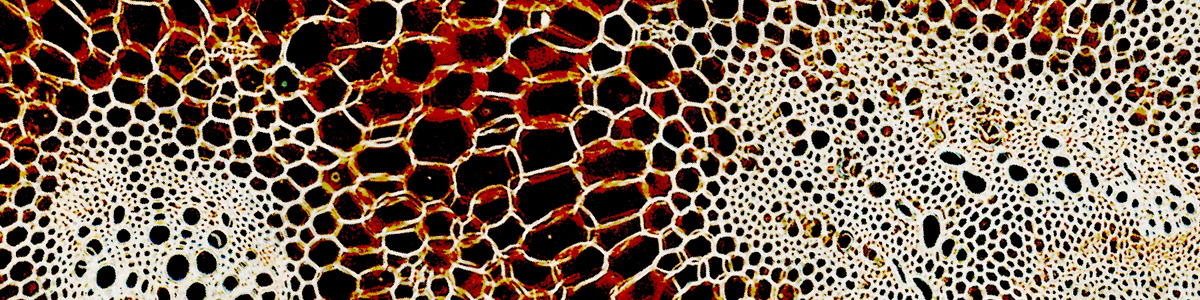
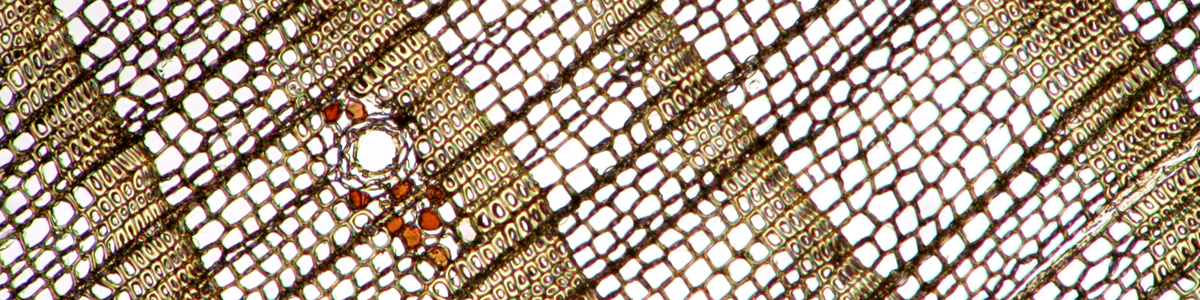
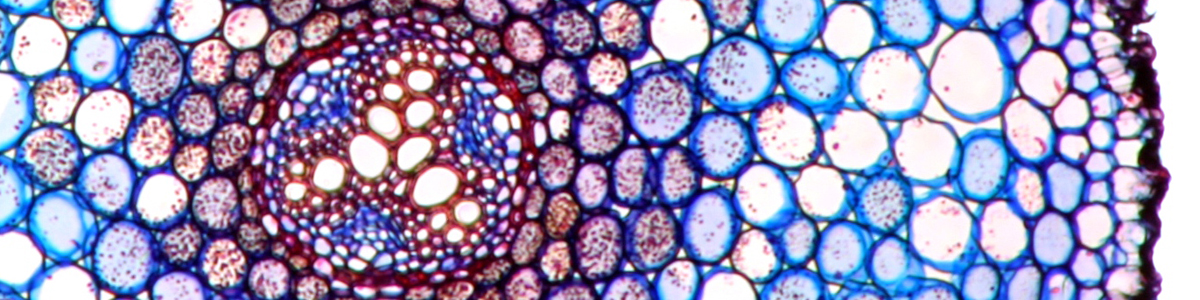
correct. LED have a much more narrow color spectrum. this is one reason why some people who do photographic work prefer the wider spectrum of halogen lamps for more natural colors. But the halogen bulb spectrum also changes with light intensity.
what about the spectrum. objects look different when LEDs are used. It seems that LEDs do not put out the full spectrum of light.
do you have any slices of prostate cancer?